Alabama Leash Laws: What You Need to Know
Alabama leash laws require dogs to be restrained when in public places. The laws vary by municipality but generally mandate leashing dogs when off the owner’s property to protect public safety.
Alabama’s statewide leash law provides a framework that cities and counties can build upon with their ordinances. Understanding the leash law requirements in your area is important for responsible pet owners. This article explains Alabama’s leash law provisions, including history, scope, penalties, changes, and controversies. It also answers common questions and provides resources on leash laws in Alabama.
When Were Alabama Leash Laws Enacted and Why
Alabama enacted its first statewide dog leash law in 1988 with the Companion Animal Statute. The law authorized municipalities to establish local leash ordinances.
The motivation behind Alabama leash law was to address public safety issues caused by uncontrolled dogs. Loose dogs can intimidate people, get hit by vehicles, attack other dogs, and threaten children. Leash laws are designed to prevent these dangers.
Specific incidents that led to statewide action include:
- Dog bites requiring medical care rose from 585 in 1987 to over 1,000 by 1990.
- Reports of loose dogs menacing neighborhoods and parks increased in the late 1980s.
- Public pressure mounted after highly publicized dog attacks.
Leash laws balance pet owners’ rights with the community’s interest in safety. Alabama determined statewide authorization was necessary for consistent enforcement.
Who Alabama Leash Laws Apply To
The state leash law and local ordinances apply to any person owning or controlling a dog in public areas. Public areas generally include:
- Streets, sidewalks, parks and trails
- Commercial areas like shopping centers
- Common areas of apartment complexes, HOAs, etc.
- Other public property not owned by the dog guardian
Leash laws do not always apply to private property. However, a dog must be leashed when off the owner’s private premises.
The laws apply to all dog guardians regardless of county or city residence. Guardians must follow leash ordinances in whatever jurisdiction they are present with the dog.
Key Provisions of Alabama Leash Laws
Alabama’s leash law establishes core requirements for dogs in public places:
- Restraint Required:- Dogs must be physically restrained by a leash, tether, or other device when in public areas. Voice control alone does not satisfy the law.
- Maximum Leash Length:- Most cities limit leashes to 6 feet or less. Extendable leashes must be locked at a compliant length when in public.
- Proper Securing:- Guardians must keep hold of the leash. Tying dogs to trees, benches, etc. often violates the law.
- Exemptions:- Working dogs like police K9s are exempt while performing duties. Service animals may be exempt in some cases under ADA rules.
- Enforcement:– Police and animal control officers enforce leash laws. They can require proof of rabies vaccination.
- Penalties:- Fines, fees, and civil citations apply. Amounts vary by city, typically $50-$150. Higher for repeat offenses.
Local Ordinances Build on State Law
While Alabama provides a baseline leash law, most enforcement occurs through local city and county ordinances:

- Birmingham – Leash law enforced in parks. up to a $500 fine.
- Montgomery – Leashes required in public. Limit 6 feet. $100 fine.
- Huntsville – Dogs must be leashed outside the owner’s property. Extendable leashes are limited to 8 feet.
- Mobile – Mandatory leashing and a $50 fine. Stiffer penalties for aggressive dogs.
- Jefferson County – Leashes up to 3 feet required. $50 first offense, up to $500 for repeat violations.
Guardians must check the specific area’s laws. Most municipalities prohibit unrestrained dogs in public areas.
Penalties for Violating Alabama Leash Laws
In Alabama, the penalties for violating leash laws may include:
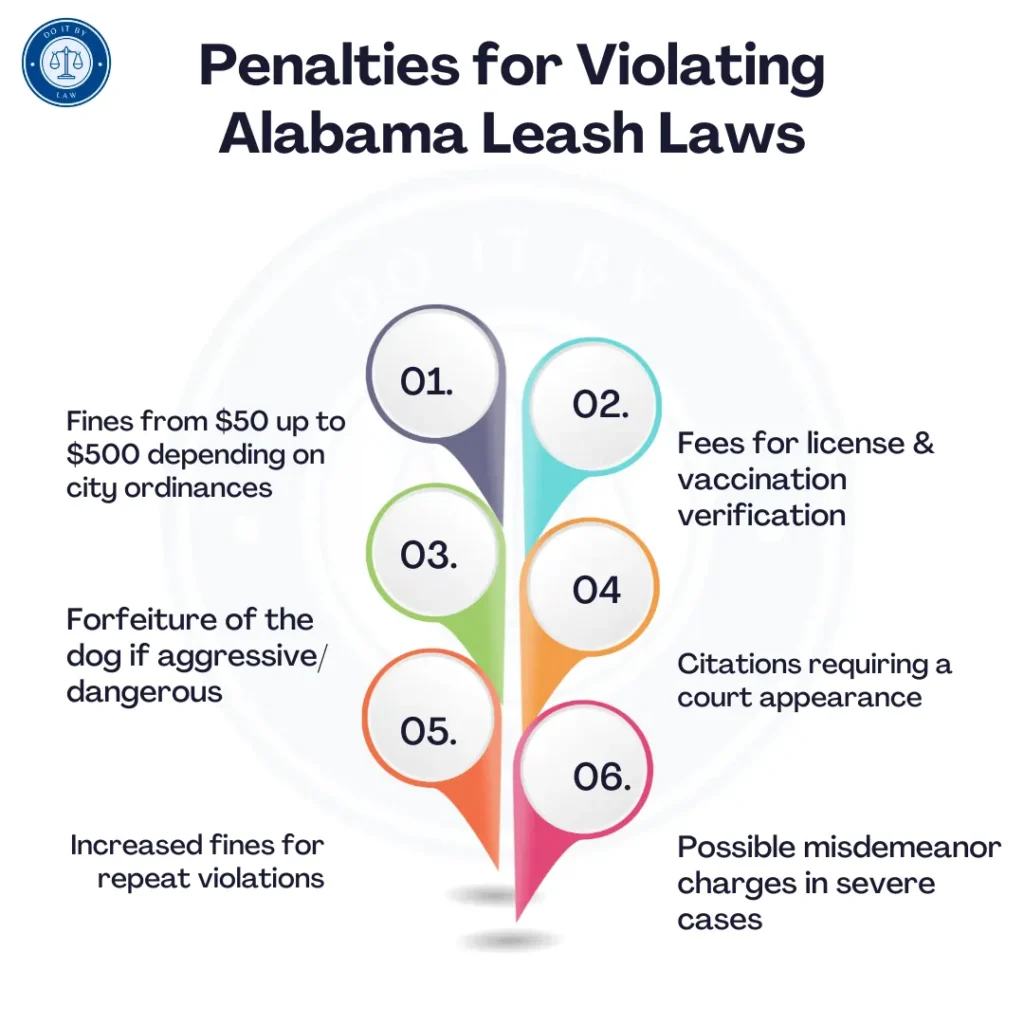
- Fines from $50 up to $500 depending on city ordinances
- Fees for license and vaccination verification
- Citations requiring a court appearance
- Forfeiture of the dog if aggressive/dangerous
- Increased fines for repeat violations
- Possible misdemeanor charges in severe cases
Leash law violations may also trigger investigations of animal cruelty, dogfighting, or other mistreatment. Courts prefer education and fines over criminalization for leash offenses. But penalties increase for recurring noncompliance.
Recent Changes to Strengthen Alabama’s Leash Laws
Some recent updates to Alabama leash laws include:
- Birmingham – Increased fines in 2020 and required leashes up to 6 feet.
- Anniston – City code revised in 2021 to mandate restraint of dogs away from owner’s premises.
- Montgomery – Ordinance passed in 2019 closing loophole on restraint requirements.
- Oxford – A new leash law enacted in 2017 requiring dogs restrained in public areas.
- Prattville – Amended code in 2014 to mandate leashing and clarify length rules.
Many cities acted in response to rising complaints about uncontrolled dogs. Strengthening leash rules aided more consistent enforcement.
Ongoing Controversies and Challenges to Leash Laws
Despite public safety goals, leash laws prompt ongoing debates similar to other states:
- Critics argue leash laws infringe on pet owners’ freedoms.
- Enforcement can be inconsistent, especially with extendable leashes.
- Rules vary widely between communities confusing.
- In rural areas, leashes may be less necessary.
- Proof of vaccination and licensure requirements are controversial.
- Service animal status provides leash exceptions that some abuse.
- Commercial dog-walking businesses often violate restraint rules.
Public pressure after serious incidents typically overrides complaints. But protests persist around perceptions of overreach and uneven enforcement.
Conclusion and Key Takeaways on Alabama Leash Laws
In summary, Alabama’s statewide leash statute sets the framework for detailed local ordinances mandating dogs be leashed in public spaces. Requirements vary across the state but serve the common purpose of preventing safety issues. Responsible pet guardians must understand their area’s specific leash rules.
Key takeaways on Alabama leash laws include:
- State law authorizes cities and counties to implement leash ordinances.
- Most municipalities require dogs leashed and secured when not on the owner’s private property.
- There are fines and citations for violations, increasing for repeat offenses.
- Updates often strengthen leash rules in response to recurring complaints.
- Some critics protest the constraints and inconsistent enforcement.
- Knowing the laws is crucial for dog guardians to avoid violations and penalties.
Following leash laws displays respect for the community. It helps ensure the welfare of pets, neighbors, and the public at large.







